In This Lesson You Will Learn What Is Google Tag Manager
The purpose of this lesson is to highlight the usability of Google Tag Manager account on websites, how it can lessen your reliance on a web developer and how it aligns your tracking with a single code on the website.
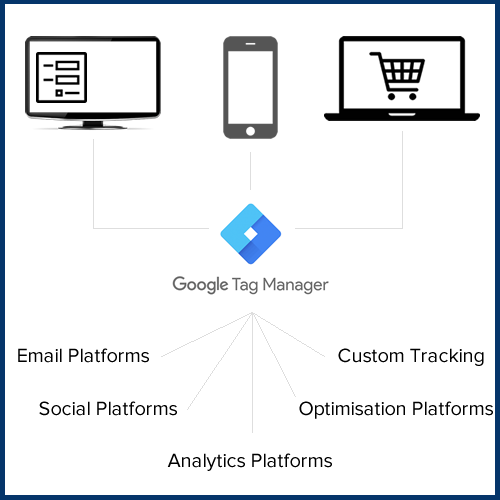
Understanding Google Tag Manager
What Is Google Tag Manager?
You may have come across many third-party platforms such as Facebook, Google, IFrame forms etc to implement snippets of codes on your website for data tracking, creating an audience or tracking conversions.
Google Tag Manager is a free tool from Google that can ease this process by bypassing the need of having a web developer at your service on standby.
It can be pretty overwhelming & costly to implement multiple snippets from different platforms individually on the website with help from a web developer.
The Google Tag Manager container stores a wide range of tags which is very handy for the marketer to manage and modify changes in one place.
Which snippets can be implemented on the website using Google Tag Manager (GTM)?
Google Tag Manager can be highly customised for different accounts and their requirements. To give an idea of the range of snippets or tracking that can be implemented on the website using the Google Tag Manager, we have added a few example tags below;
- Google Analytics code, whether it is the new gtag or universal code.
- Google Ads - Conversion tag
- Google Ads - Audience Remarketing tag
- Google Analytics - Events & Goal tracking
- Google Analytics - Standard ECommerce, Enhanced ECommerce & UserID tracking (with few implementations from your web developer or CMS)
- Facebook - Audience Pixel, Conversion Pixel, FB Analytics tracking
- LinkedIn - Audience Pixel & Conversion Pixel Insights code
- MailChimp subscriber form tracking
- Conversion Rate Optimisation Platforms snippets and variations / Google Optimise
- Bing Ads Universal tracking
- Pinterest tag
- Twitter universal website tag & more.
What to consider before installing Google Tag Manager
We have put together a few points that you should consider before implementing Google Tag Manager on your website.
- Strategy - It is important to strategise the GTM implementation on your website in advance. Do you have multiple domains or subdomains? Do you need one container or multiple containers for implementations? Which third party tags are to be implemented?
- Installation - Most CMS platforms provide plugins, add ons to implement the GTM code on your website. In some cases, you may require to edit the page template to add the code to ensure it is implemented on all pages on the website. Ensure the code is implemented following the requirements as per the GTM interface.
- Checking the Installation - Once the code is implemented, you can review the set up by checking the ‘page source’ of a page on your website (search for ‘GTM’) or you can also install ‘Google Tag Assistant’ in your chrome browser.
- User Management - Ensure you have the owner/admin access to the Google Tag Manager platform. Based on the agencies you are working with, you can delegate different access levels to your team and third party agencies. Have a strategy that will help to ensure that if someone leaves your organization and their account credentials are terminated, the organization will maintain access to your Tag Manager account.
- Naming Protocols - Following a strict naming protocol for the tags, triggers and variables will help you in the long run. Most websites will use only one GTM account in their lifetime. It will help to understand the setup when multiple users are implementing tracking on the website for third party platforms. Using Folders and different workspaces also help to understand the setup.
- Event strategy document - You may find it useful to maintain an Event strategy document for naming the events in Google Analytics. It also helps different teams or users to adhere to existing naming for events and not invent something that will make it hard to decipher the reports.
If you are having an issue, we can help. Please get in touch.
Both platforms perform similar functions, implementing Google and third-party tags on the website.
Google Tag Manager implements the tags using a separate web interface whereas Global Site Tag implements the tag directly on the web pages using javascript.
Go to your website and right-click > ‘view page source’. Use the search option (Cmd+F Or Ctrl +F) for ‘GTM’. You will see the code for GTM highlighted for you.
You can also use an add-on in your chrome browser ‘Google Tag Assistant’ to check the GTM tag implemented on the website.
Go to your Google tag manager account, select the correct container name for your website.
In the top menu, you will see a link for ‘GTM - XXXXXX’. Select this to reveal the Google Tag Manager snippet that you can share with your web developer. Ensure to copy the code and not send a screenshot for installation.